How To Migrate MariaDB databases to another drive in Ubuntu
Migrating MariaDB databases to another drive in Ubuntu
Overview
This example explains how to migrate MariaDB databases from /var/lib/mysql to /opt/mysql on an Ubuntu 22.04 server. This is a good option for a growing database that would allow for easy management and security.
Step By Step
First step of the process is to stop MariaDB.
# sudo systemctl stop mariadb
Copy the databases
Copy the existing database directory, /var/lib/mysql, to the new location, /opt/mysql, with rsync. Using the -a flag preserves the permissions and other directory properties, while-v provides verbose output so you can follow the progress:
# sudo rsync -avzh /var/lib/mysql /opt/
Once the rsync command is complete, rename the current folder with a .bak extension and keep it until you’ve confirmed the move was successful. By renaming it, you’ll avoid confusion that could arise from files in both the new and the old location
# sudo mv /var/lib/mysql /var/lib/mysql.bak
Change MariaDB Configuration
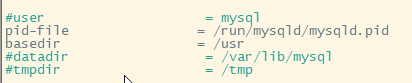
Next change /etc/mysql/mariadb.conf.d/50-server.cnf to point to the new database location.
# nano /etc/mysql/mariadb.conf.d/50-server.cnf
Un-comment #datadir line and change /var/lib/mysql to /opt/mysql
Before
After
Configuring AppArmor
Now, you have to configure AppArmor to allow /db to be a MySQL/MariaDB data directory.
To do that, edit the AppArmor alias file /etc/apparmor.d/tunables/alias as follows:
# nano /etc/apparmor.d/tunables/alias
Uncomment # alias and change /home/mysql to /opt/mysql
Before
After
Restart apparmor
# systemctl restart apparmor
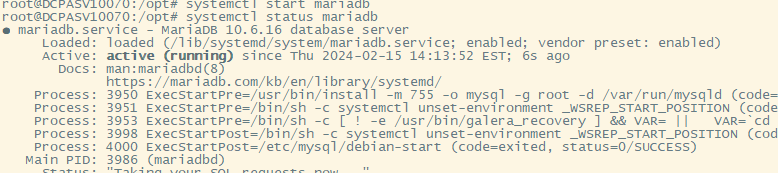
Restart Mariadb
# systemctl start mariadb
Checking The Results
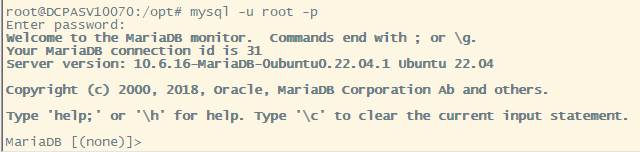
Connect to the DB and verify the changes
# mysql -u root -p
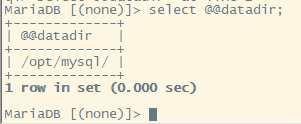
Run a query command to verify MariaDB is using the correct DB directory
select @@datadir;
List database
show databases;
Exit out by typing exit.













Leave a Reply